10th IUFRO Wind and Trees Conference

The triannual IUFRO Wind and Trees Conference organised by IUFRO Unit 8.0.3.06 was held in Castelfranco Veneto from 20 to 23 June 2023. The meeting was hosted by the University

The triannual IUFRO Wind and Trees Conference organised by IUFRO Unit 8.0.3.06 was held in Castelfranco Veneto from 20 to 23 June 2023. The meeting was hosted by the University
Caught between a rising demand for timber, the difficulty of meeting national carbon reduction targets and pressure from environmentalists who have secured a ban on all timber harvesting in native

The IUFRO Division 7 (Forest Health. Pathology and Entomology) Conference took place in Lisbon from the 6th to 9th September 2022, with 350 participants present (and 60 remote participants) from

On Wednesday, December 7, 2022, IEFC in collaboration with AgroParisTech Nancy and the IFSA FRANCE Association, organised an evening of discussion on participatory science tools for forests (Assessment, Issues &
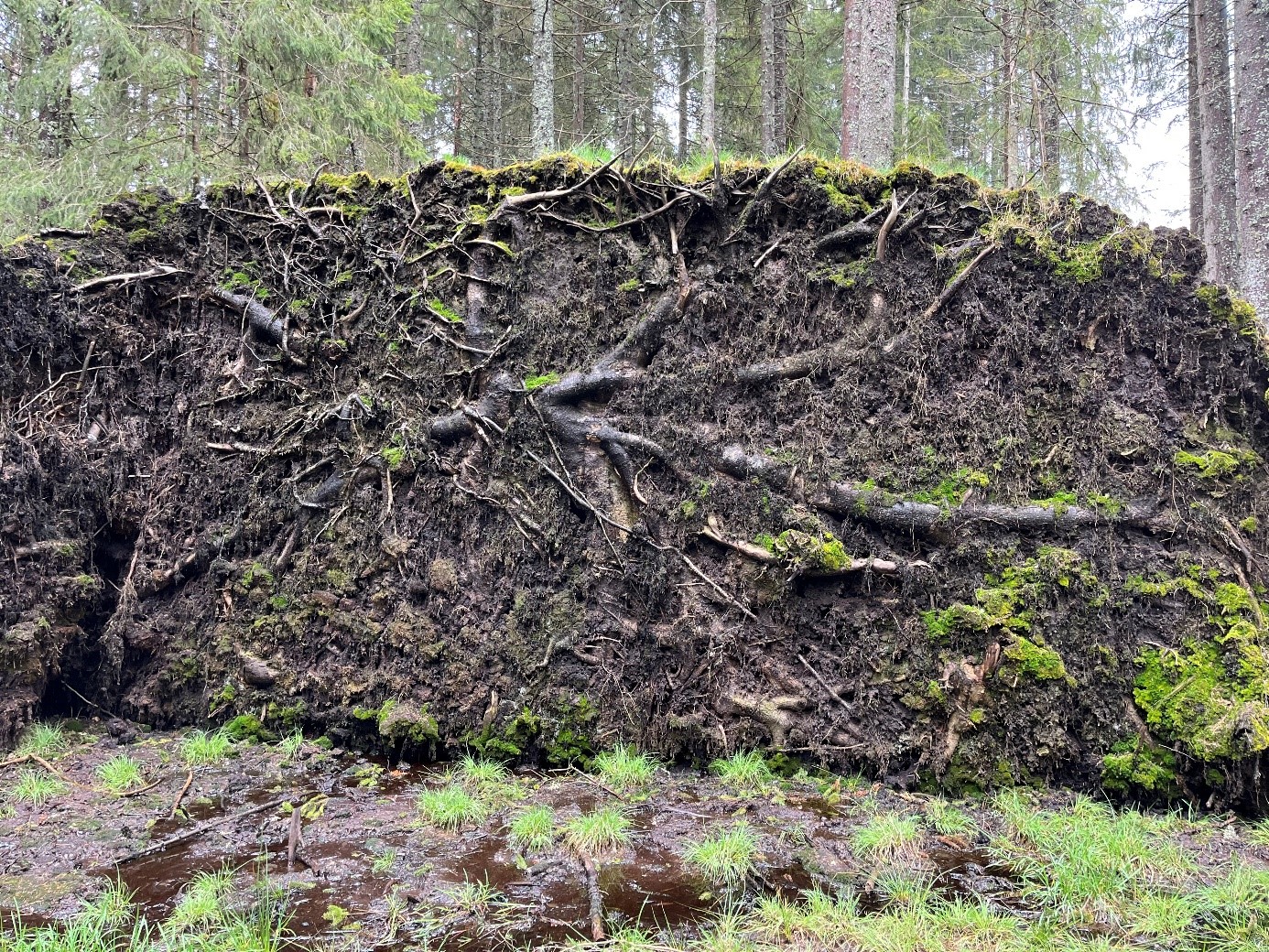

Optimizing forest allocation asks not only for integration of multiple services but also taking into account multiple risks affecting forest processes and functions (Yousefpour et al. 2017). Moreover, climate change
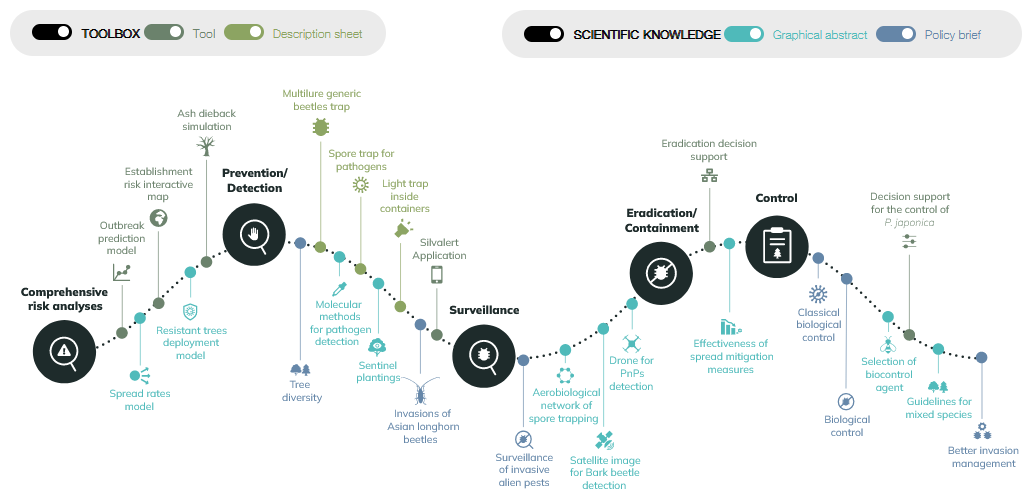
The risk of introducing non-native Pests and Pathogens (PnPs) into Europe has increased exponentially since the 1800s1 . The main reasons are, on the one hand the rise in trade
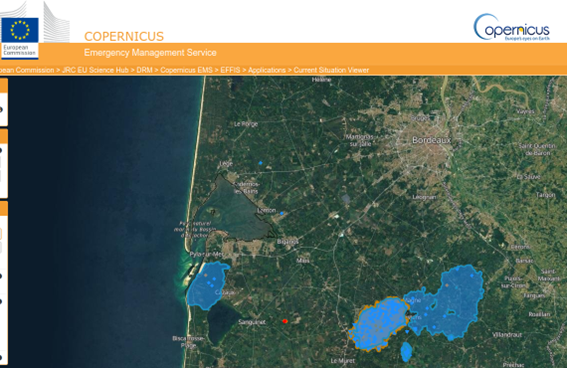
The FIRE-RES project aims to provide the EU with the capacity to manage the projected increase in forest fires under a harsher climate. It will deploy a series of innovation
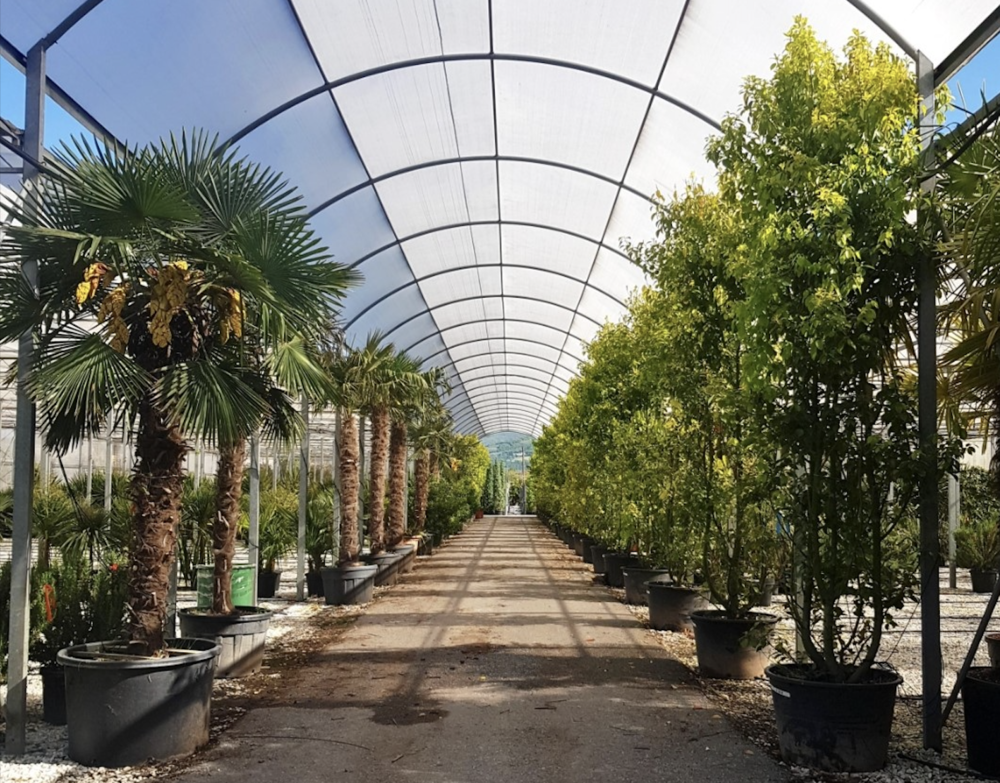

On the 28th of April 2022, a dozen participants from all over Europe gathered in Pistoia, Italy – one of the most important areas for nursery plant production – to